Summary :
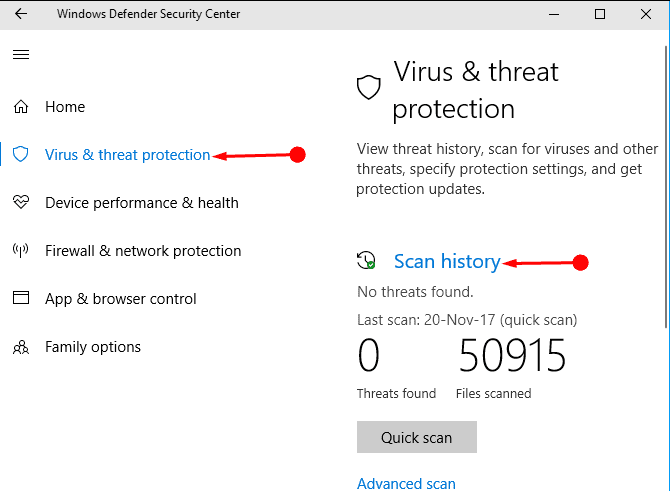
Have you ever seen the error message: There is a problem with this drive? Scan the drive now and fix it? Actually, this may appear after you connected a USB drive or SD card to a computer. Windows thinks there is something wrong with that drive, so it advises you to scan the disk and fix it by calling the built-in disk check tool.
Quick Navigation :
When you plug in a removable device to the computer running Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, or Vista, an error may occur to inform you that you there’s a problem with this drive and you need to scan it & fix it. Naturally, most people are prone to start the scan and fix process as the system suggests.
Unable To Scan Recovery Disk Assistant.dmg Internal Error Windows 7
Apr 15, 2016 How To Connect Two Routers On One Home Network Using A Lan Cable Stock Router Netgear/TP-Link - Duration: 33:19. Richard Lloyd Recommended for you.
- Sometimes, no error will be found after the scan.
- Yet, if any errors are found on this drive, Windows will advise you to repair the drive by offering an error checking window, on which you can click to Repair drive easily.
Now, here comes the question: what if Windows was unable to repair the drive? How are you going to deal with such a terrible situation? My advice is recovering data firstly when Window can't repair this drive. Then, try any method that works to fix the issue properly.
Windows Was Unable to Repair the Drive: Error Occurs
Some of you may curious about: how do I scan and fix my drive, right? Actually, there is a check disk utility integrated into all Windows systems (the CHKDSK error checking) as many people know. To be specific, this disk checking tool aims at checking logical and physical errors on the file system and file system metadata of certain drive.
Well, does scan and fix delete files? Does repair drive erase data? Undeniably, it may do. So you are expected to read this so as to gain the skills of deleted files recovery after the scan and fix:
It is shocking when you find Windows Scan and Fix deleted files that you need, but it is not the end of the world since you can get remedies for it.
Error Messages
Though you can click to repair the drive after the error checking scan, you may end up in failure:
- There was a problem repairing this drive.
- There was a problem repairing this drive SD card.
- Windows was unable to repair the drive USB.
- Windows can’t repair the drive while it’s in use.
The full error may be something like: There was a problem repairing this drive. Windows was able to repair the drive. Close this dialogue box, and then try to repair the drive again.
The most direct way to try to fix this is:
- Eject the drive from your computer properly.
- Restart your computer.
- Connect it again after the PC restarted.
Most of the time, the quick restart won’t work. So you need to recover data from this drive immediately and then follow the solutions that will be mentioned later carefully.
Real Case
How to fix this error 'There was a problem repairing this drive'?
I've looked all over the web, and can't find a solution to this one. I have Windows 8 and get this error message every time I plug anything into my usb port: There's a problem with this drive. Scan the drive now and fix it. Whether it's my iPod, flash drive, any usb-I get this window in the upper right of the screen. Everything I plug in works and is fine, and there is no problems with the devices. At least the window goes away in about 5-6 seconds. Still, it would be nice if it didn't show up at all. (It would also be nice to win the lottery, but I can't always have everything I want!) Is there a way to not have this window pop up?- from bigoldcars in Microsoft Community
Recover Data at Once When Window Can't Repair the Drive
Reasons for USB Drive Data Recovery
Why the USB data recovery from the check program error is necessary? Two main reasons are:
- It’s very likely that there will be some files lost during the scan and repair process.
- In order to fix the Window can't repair this drive, you’ll need to accomplish a lot of operations, which can easily lead to data loss.
Steps of the USB Device Recovery
How to recover a deleted scanned document:
Step 1: find a piece of reliable data recovery software and get it downloaded properly (download it from the official website; don’t open some suspicious links at will). MiniTool Power Data Recovery is trusted by over 2 million people; if you doubt this, you may use the Trial Edition of version 8.1 at first.
Step 2: install the trial edition by double clicking on the setup application. Then, launch it to see the following window.
Generally, this page will only appear for a few seconds and then you will be brought to the main interface of the software.
Step 3: please select an option from This PC, Removable Disk Drive, Hard Disk Drive, and CD/DVD Drive.
- This PC option helps to display all the partitions that are mounted to the computer.
- Removable Disk Drive is used to display all the removable devices, such as USB flash drive, USB external hard drive, or SD card (here’s how to recover deleted files from USB).
- In Hard Disk Drive, only the hard disk drives (both internal and external) will be shown.
- Obviously, the CD/DVD Drive option is designed for only the optical discs like CD and DVD.
- Apparently, you should choose This PC if the target drive is only a partition on the internal/external hard disk, memory card, or the flash drive.
- Well, if the target device is a hard disk/flash disk that contains more than one partition, you may choose Removable Disk Drive or Hard Disk Drive.
Step 4: specify the drive that Windows prompts it can’t repair. Then double click on it or just click on the Scan button to start detecting files in it. Then, you’ll see the window as shown below.
Here, you can click to browse the currently found files any time during the scan. Yet, as the prompt says, if you’d like to get the best recovery result, you may as well wait till the end of the scan.
Step 5: once you have found the deleted scanned document that you need, you should add a check mark into the square box in front of it. Then, when you have selected all the files you need, you should click on the Save button to choose a safe storage path for them (don’t save them to the original place which Windows fails to repair). At last, please click on the OK button to confirm the storage path.
When all files have been saved to the appointed place successfully, a prompt window will appear in the software. At this time, you can close the software and put an end to the recovery.
If you’d like to learn more details on how to fix a broken USB stick and recover data, please go to this page:
The question of how to fix a broken USB stick is not difficult to answer when the damage is caused by logical errors.
Possible Causes
After an investigation, I found 3 main causes for the unrepairable drive issue:
- Disconnect the USB device from your computer forcibly (you are advised to safely remove the USB device).
- Get attacked by the virus since you use the USB drive across different devices and platforms (use it on different PCs, game consoles, or cameras).
- There’s something wrong with the file system of the USB drive (The file or directory is corrupted and unreadable, fatal device hardware error, etc.).
Fix Error: Windows Was Unable to Repair the Drive
The Windows snap-in Error Checking or CHKDSK tool is mainly used to scan the partitions and disk drives mounted on the computer for disk errors or bad sectors. Once the problem is found, it will offer solutions to help you repair the error in order to make the drive working properly again. You just need to finish a few clicks to scan the disk and repair the error.
But, if the system says it can’t repair the drive for you, you need to turn to the following solutions for fixing the problem after recovering data after CHKDSK. (Please note that all the operations below are performed in a Windows 10 computer.)
Solution 1: Run Disk Check in Command Prompt
- Click on the Cortana icon/search box from the left corner of the taskbar.
- Type command prompt into the text box.
- Right click on Command Prompt (Desktop app) from the Best match area.
- Choose Run as administrator from the right-click menu.
- Select Yes in the pop-up User Account Control window so as to allow this app to make changes to your device.
- Type chkdsk *: /r and press Enter (this command helps to locate the bad sectors on the target disk, analyze physical disk errors, and recover readable information; but you need to remember that the target disk must be locked).
- Wait for the check disk process to complete (if any problems are found, the system will fix them automatically).
Solution 2: Run System File Checker Tool
- Repeat step 1 ~ 5 mentioned in solution 1 or run the command prompt as administrator by another way.
- In the Administrator: Command Prompt window, type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
- Wait for the completion of the scan and exit command prompt at the end.
- Restart your PC and go to check for any improvements.
Solution 3: Troubleshoot Hardware and Devices
In all Windows systems, there is a Hardware and Devices troubleshooter, designing for fixing errors with storage devices. Here’s how to use it:
- Click on the Windows Start button in the lower left corner of the screen.
- Scroll down to find the Windows System folder.
- Click to expand this folder and choose Control Panel within it.
- Choose to View by Small icons.
- Choose Troubleshooting from listed items.
- Find Hardware and Sound from the right-side pane.
- Click on the Configure a device option under it.
- Click on the Advanced option in the pop-up window so as to Apply repairs automatically.
- Click on the Next button and then follow the instructions to finish the repair process.
Solution 4: Run Startup Repair
The Startup Repair is also a popular tool built in Windows. Its main function is to scan and repair the errors that may break off the loading process of the computer system. Here’s how to use it:
- Click on the Windows Start button.
- Scroll down to select Settings option.
- Choose Update & Security (Windows Update, recovery, backup).
- Select Recovery from the left-hand pane.
- Find the Advanced startup section from the right pane.
- Click on the Restart now button.
- Click on the Troubleshoot button from Choose an option window.
- Select the Advanced options from Troubleshoot window.
- Click on the Startup Repair button from Advanced options window.
- Select the correct account and type the corresponding password.
- Click on the Continue button and wait for the scanning/problem detecting process.
- If any problem is found, the tool will fix it.
Click here to see how to access Advanced startup in different cases.
That’s all I want to say about how to fix the Window can't repair this drive/check program error. Of course, there are other possible fixes like running a diagnostic tool and a clean install of Windows. You may follow them step by step to try to solve the problem yourself.
Conclusion
Unable To Scan Recoverydiskassistant.dmg Internal Error Download
It’s a normal thing to see a Windows prompt on your computer. Sometimes, the message only informs you of some information; while in other cases, it may indicate a series of problems found by the system. For instance, Windows was unable to repair the drive is a popular error message to show that there’s a problem fixing the found error on the target device.
What’s the right thing to do at this time? My suggestions are:
- Close the prompt window and recover data from it immediately with a reliable tool.
- Then, you may analyze your problem and try the possible solutions to try to make it right.
If you still can’t repair the error after reading this, please feel free to leave a message below, describing your situation in detail.
Windows Was Unable to Repair the Drive FAQ
- Right click on This PC/Computer icon on the desktop.
- Choose Manage from the context menu.
- Click Disk Management under Storage.
- Look through the disks & partitions list and pick out the problematic drive.
- Right click on it and choose Format.
- Wait for the process to finish.
- If this didn't work, please use Format Partition of MiniTool Partition Wizard.
- Run CHKDSK in Command Prompt to repair logical problems.
- Check the drive for errors by clicking Check under Error checking.
- Run a scan under Maintenance in Control Panel.
- Recover data from the corrupted hard drive and then reformat it.
You can convert RAW to NTFS without formatting by using the Command Prompt tool.
- Open Windows search textbox and type cmd.
- Right click on Command Prompt from search result.
- Choose Run as administrator from the pop-up menu.
- Type Diskpart and press Enter.
- Type *: /FS :NTFS (* is the drive letter) and press Enter.
Related
Introduction
When accessing a web server or application, every HTTP request that is received by a server is responded to with an HTTP status code. HTTP status codes are three-digit codes, and are grouped into five different classes. The class of a status code can be quickly identified by its first digit:
- 1xx: Informational
- 2xx: Success
- 3xx: Redirection
- 4xx: Client Error
- 5xx: Server Error
This guide focuses on identifying and troubleshooting the most commonly encountered HTTP error codes, i.e. 4xx and 5xx status codes, from a system administrator’s perspective. There are many situations that could cause a web server to respond to a request with a particular error code–we will cover common potential causes and solutions.
Client and Server Error Overview
Client errors, or HTTP status codes from 400 to 499, are the result of HTTP requests sent by a user client (i.e. a web browser or other HTTP client). Even though these types of errors are client-related, it is often useful to know which error code a user is encountering to determine if the potential issue can be fixed by server configuration.
Server errors, or HTTP status codes from 500 to 599, are returned by a web server when it is aware that an error has occurred or is otherwise not able to process the request.
General Troubleshooting Tips
- When using a web browser to test a web server, refresh the browser after making server changes
- Check server logs for more details about how the server is handling the requests. For example, web servers such as Apache or Nginx produce two files called
access.loganderror.logthat can be scanned for relevant information - Keep in mind that HTTP status code definitions are part of a standard that is implemented by the application that is serving requests. This means that the actual status code that is returned depends on how the server software handles a particular error–this guide should generally point you in the right direction
Now that you have a high-level understanding of HTTP status codes, we will look at the commonly encountered errors.
400 Bad Request
The 400 status code, or Bad Request error, means the HTTP request that was sent to the server has invalid syntax.
Here are a few examples of when a 400 Bad Request error might occur:
- The user’s cookie that is associated with the site is corrupt. Clearing the browser’s cache and cookies could solve this issue
- Malformed request due to a faulty browser
- Malformed request due to human error when manually forming HTTP requests (e.g. using
curlincorrectly)
401 Unauthorized
The 401 status code, or an Unauthorized error, means that the user trying to access the resource has not been authenticated or has not been authenticated correctly. This means that the user must provide credentials to be able to view the protected resource.
An example scenario where a 401 Unauthorized error would be returned is if a user tries to access a resource that is protected by HTTP authentication, as in this Nginx tutorial. In this case, the user will receive a 401 response code until they provide a valid username and password (one that exists in the .htpasswd file) to the web server.
403 Forbidden
The 403 status code, or a Forbidden error, means that the user made a valid request but the server is refusing to serve the request, due to a lack of permission to access the requested resource. If you are encountering a 403 error unexpectedly, there are a few typical causes that are explained here.
File Permissions
403 errors commonly occur when the user that is running the web server process does not have sufficient permissions to read the file that is being accessed.
To give an example of troubleshooting a 403 error, assume the following situation:
- The user is trying to access the web server’s index file, from
http://example.com/index.html - The web server worker process is owned by the
www-datauser - On the server, the index file is located at
/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
If the user is getting a 403 Forbidden error, ensure that the www-data user has sufficient permissions to read the file. Typically, this means that the other permissions of the file should be set to read. There are several ways to ensure this, but the following command will work in this case:
.htaccess
Another potential cause of 403 errors, often intentinally, is the use of an .htaccess file. The .htaccess file can be used to deny access of certain resources to specific IP addresses or ranges, for example.
If the user is unexpectedly getting a 403 Forbidden error, ensure that it is not being caused by your .htaccess settings.
Index File Does Not Exist
If the user is trying to access a directory that does not have a default index file, and directory listings are not enabled, the web server will return a 403 Forbidden error. For example, if the user is trying to access http://example.com/emptydir/, and there is no index file in the emptydir directory on the server, a 403 status will be returned.
If you want directory listings to be enabled, you may do so in your web server configuration.
404 Not Found
The 404 status code, or a Not Found error, means that the user is able to communicate with the server but it is unable to locate the requested file or resource.
404 errors can occur in a large variety of situations. If the user is unexpectedly receiving a 404 Not Found error, here are some questions to ask while troubleshooting:
- Does the link that directed the user to your server resource have a typographical error in it?
- Did the user type in the wrong URL?
- Does the file exist in the correct location on the server? Was the resource was moved or deleted on the server?
- Does the server configuration have the correct document root location?
- Does the user that owns the web server worker process have privileges to traverse to the directory that the requested file is in? (Hint: directories require read and execute permissions to be accessed)
- Is the resource being accessed a symbolic link? If so, ensure the web server is configured to follow symbolic links
500 Internal Server Error
The 500 status code, or Internal Server Error, means that server cannot process the request for an unknown reason. Sometimes this code will appear when more specific 5xx errors are more appropriate.
This most common cause for this error is server misconfiguration (e.g. a malformed .htaccess file) or missing packages (e.g. trying to execute a PHP file without PHP installed properly).
502 Bad Gateway
The 502 status code, or Bad Gateway error, means that the server is a gateway or proxy server, and it is not receiving a valid response from the backend servers that should actually fulfill the request.
If the server in question is a reverse proxy server, such as a load balancer, here are a few things to check:
- The backend servers (where the HTTP requests are being forwarded to) are healthy
- The reverse proxy is configured properly, with the proper backends specified
- The network connection between the backend servers and reverse proxy server is healthy. If the servers can communicate on other ports, make sure that the firewall is allowing the traffic between them
- If your web application is configured to listen on a socket, ensure that the socket exists in the correct location and that it has the proper permissions
503 Service Unavailable
The 503 status code, or Service Unavailable error, means that the server is overloaded or under maintenance. This error implies that the service should become available at some point.
If the server is not under maintenance, this can indicate that the server does not have enough CPU or memory resources to handle all of the incoming requests, or that the web server needs to be configured to allow more users, threads, or processes.
504 Gateway Timeout
The 504 status code, or Gateway Timeout error, means that the server is a gateway or proxy server, and it is not receiving a response from the backend servers within the allowed time period.
This typically occurs in the following situations:
- The network connection between the servers is poor
- The backend server that is fulfilling the request is too slow, due to poor performance
- The gateway or proxy server’s timeout duration is too short
Unable To Scan Recoverydiskassistant.dmg Internal Error File
Conclusion
Now that you are familiar with the most common HTTP error codes, and common solutions to those codes, you should have a good basis for troubleshooting issues with your web servers or applications.
If you encounter any error codes that were not mentioned in this guide, or if you know of other likely solutions to the ones that were described, feel free to discuss them in the comments!